
Various rules of thumb may be used to decide whether "n" is large enough. If "n" is large enough, the skew of the distribution is not too great, and a suitable continuity correction is used, then an excellent approximation to B("n", "p") is given by the normal distribution
#Binomial cdf formula free#
Register free for online tutoring session to clear your doubts. What is a Cumulative Distribution Function CDF of a random variable ‘X’ is a function which can be defined as, FX(x) P(X x) The right-hand side of the cumulative distribution function formula represents the probability of a random variable ‘X’ which takes the value that is less than or equal to that of the x. Various other probabilities can then be calculated using the proposition on cdf’s. Learn about Binomial Expansion Formula topic of maths in details explained by subject experts on. Appendix Table A.1 tabulates the cdf F(x) P(X x) for n 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 in combination with selected values of p. If "X" ~ B("n", "p") and "Y" ~ B("m", "p") are independent binomial variables, then "X" + "Y" is again a binomial variable its distribution is Using Binomial Tables Even for a relatively small value of n, the computation of binomial probabilities can be tedious. In probability theory, the binomial distribution comes with two parameters.


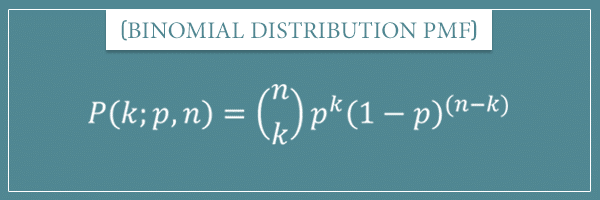
To recall, the binomial distribution is a type of probability distribution in statistics that has two possible outcomes. p: The probability of success on an individual trial. Where, n: is the number of trials x: The number of successes that result from the binomial experiment. y F ( x n, p ) i 0 x ( n i ) p i ( 1 p ) ( n i ) I ( 0, 1, , n ) ( i ). Binomial Distribution Formula: Binomial Distribution Formula is shown below. Parameters = n geq 0 number of trials ( integer)Ĭdf = I_(X))^2= (n^2p^2 - np^2 + np) - n^2p^2 = np(1 - p). The binomial distribution formula helps to check the probability of getting x successes in n independent trials of a binomial experiment. In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters n and p is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of n independent experiments, each asking a yesno question, and each with its own Boolean-valued outcome: success (with. What is the binomial CDF formula The binomial cumulative distribution function lets you obtain the probability of observing less than or equal to x successes in n trials, with the probability p of success on a single trial.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
